Jasper Alblas
Jasper Alblas
Mastering Data & Cybersec
Welcome to this walkthrough of the Phishing Analysis Fundamentals Room on TryHackMe. In this room we learn about how to analyze phishing attacks. Phishing is a common social engineering attack and is the fraudulent practice of sending emails or other messages purporting to be from reputable companies in order to induce individuals to reveal personal information

Room URL:
https://tryhackme.com/room/phishingemails1tryoe
I am making these walkthroughs to keep myself motivated to learn cyber security, and ensure that I remember the knowledge gained by these challenges on HTB and THM. Join me on learning cyber security. I will try and explain concepts as I go, to differentiate myself from other walkthroughs.
Now, let’s move on! This is going to be a long one!
Spam and phishing are both widespread social engineering attacks, but phishing through email is especially dangerous. Spam has been around since the first unsolicited email in 1978 and continues to clutter inboxes today, often as a nuisance but sometimes carrying risks. Phishing, however, is more serious because attackers craft emails designed to trick users into clicking malicious links or downloading harmful attachments. Even with strong, layered defenses in place, a single unsuspecting employee can give attackers access to a corporate network.
Security tools help reduce the number of malicious emails that reach users, but they are not perfect. This is why Security Analysts play a crucial role: they must investigate suspicious emails, determine whether they are malicious or benign, and gather intelligence to update defenses. By analyzing email headers and understanding how messages travel across the Internet, analysts can strengthen protections and prevent similar threats from reaching inboxes in the future. Practical exercises, such as dep.
Answer: No answer needed
Here’s a concise summary of the passage:
Easy. 1970s 🙂
Answer: 1970s
Three main protocols make email communication possible:
This flow ensures emails can be reliably sent, routed, and accessed securely across the internet.
You can find the following 3 answers at the page linked in the room:
https://help.dreamhost.com/hc/en-us/articles/214918038-Email-client-configuration-overview
But for your convenience I wrote them in the above summary. The port used for secure SMTP transport is 587.
Answer: 587
The port used is 993.
Answer: 993
The POP3 port for secure transport is 995.
Answer: 995
Every email has two main components:
Emails follow a standard syntax called the Internet Message Format (IMF).
When analyzing suspicious emails, start with the basics:
These are visible in most email clients.
Looking at the raw header reveals much more detail. It may look intimidating, but focus on important fields:
👉 Example: An email might show From: newsletters@ant.anki-tech.com, but the Reply-To is reply@ant.anki-tech.com. This mismatch can be a red flag.
.eml files and reviewing headers line by line.Below is an additional resource from Media Template on how to analyze email headers:
Note: The questions below are based on the Media Template article.
To find this answer we need to look at the provided URL:
https://web.archive.org/web/20221219232959/https://mediatemple.net/community/products/all/204643950/understanding-an-email-header
Here it is stated that the Return-Path email header is the one we need:
The email address for return mail. This is the same as “Reply-To:”.
Answer: Return-Path
The article once more provides the answer:
Once the email sender’s IP address is found, you can search for it at http://www.arin.net/. You should now be given results letting you know to which ISP (Internet Service Provider) or webhost the IP address belongs. Now, if you are tracking a spam email, you can send a complaint to the owner of the originating IP address. Be sure to include all the headers of the email when filing a complaint.
Answer: http://www.arin.net/.
We need to look at the following screenshot of the email body source code:
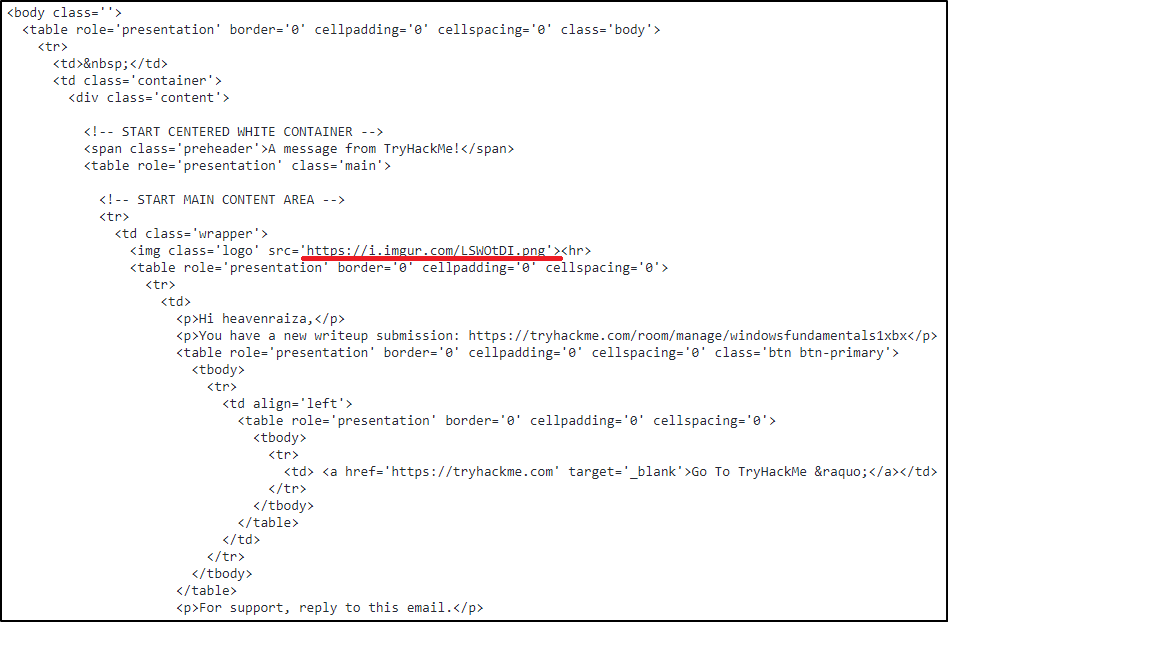
Look carefully, and you will find a img tag. Look at the src parameter value and you will see the answer.
Answer: https://i.imgur.com/LSWOtDI.png
This time, let’s look at this screenshot:
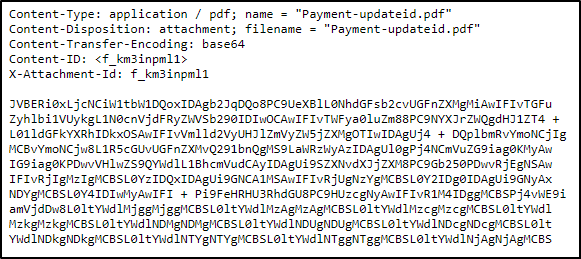
The name of the pdf file is in the top right.
Answer: Payment-updateid.pdf
Go ahead and start up the machine on TryHackMe. Now, open up the email2.txt file found on the Desktop in the Email Samples folder. Copy the base64 string. Don’t copy the last line and the header fields.
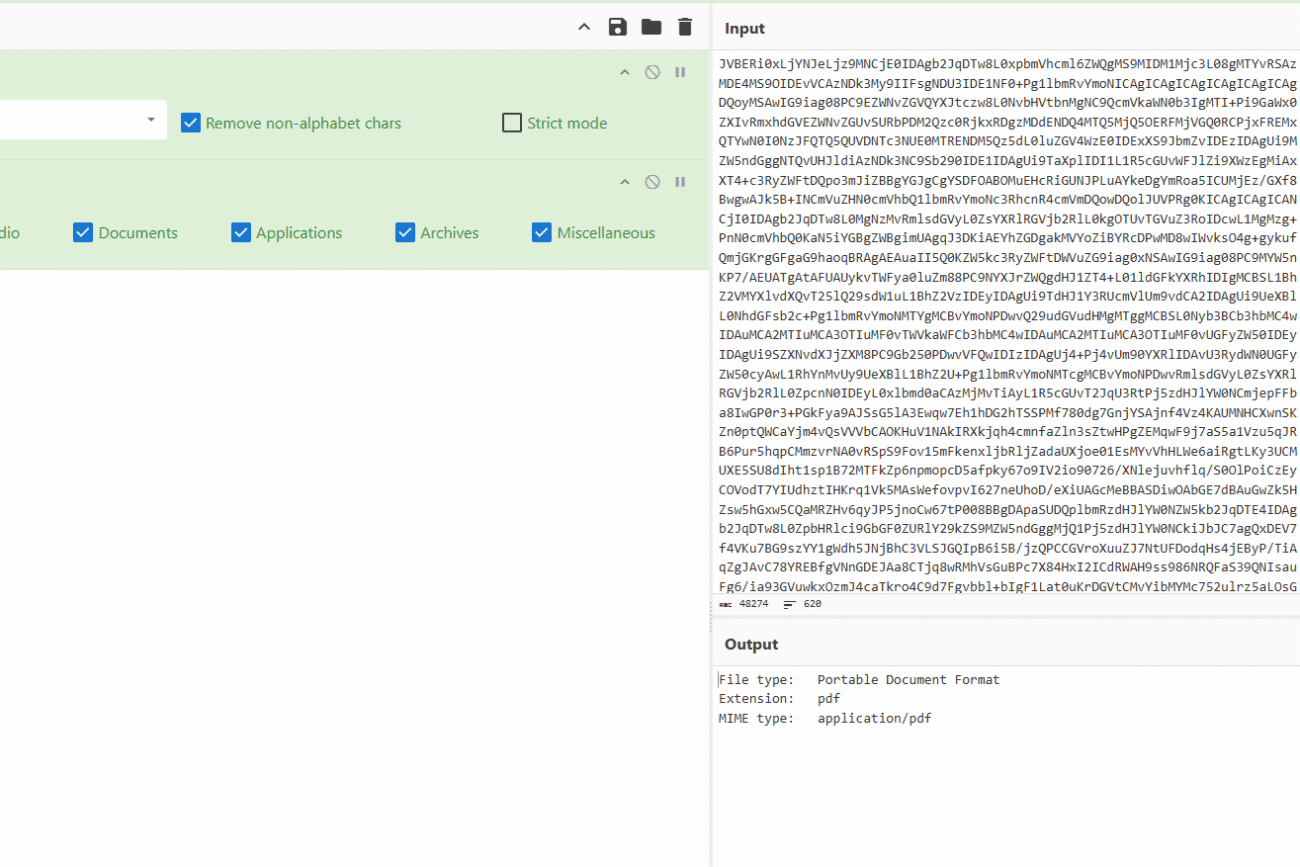
You can decode the base64 with CyberChef:
https://gchq.github.io/CyberChef/
Use the From Base64 recipe, found at the top of the left menu. Then go ahead and paste the base64 string in the input fields. You should see the PDF file within the output field now, which you should be able to download, but I had problems with it.
Alternatively you can save the base64 in a file and use: base64 -d base64.txt > output.pdf like so:
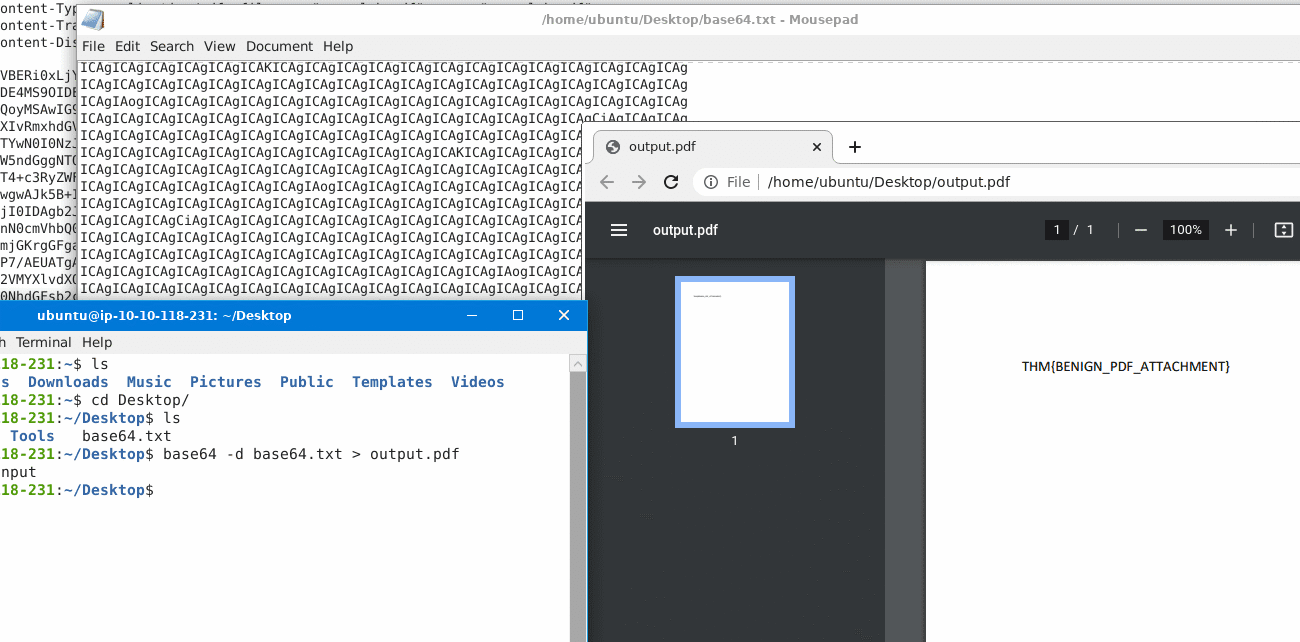
Anyway, you should have the answer now.
Description for this block. Use this space for describing your block. Any text will do. Description for this block. You can use this space for describing your block.
Answer: THM{BENIGN_PDF_ATTACHMENT}
http://www.suspiciousdomain.com → hxxp[://]www[.]suspiciousdomain[.]com.Analyze the email titled email3.eml within the virtual machine and answer the questions below.
Note: Alexa is the victim, and Billy is the analyst assigned to the case. Alexa forwarded the email to Billy for analysis.
Open the email3.eml file:
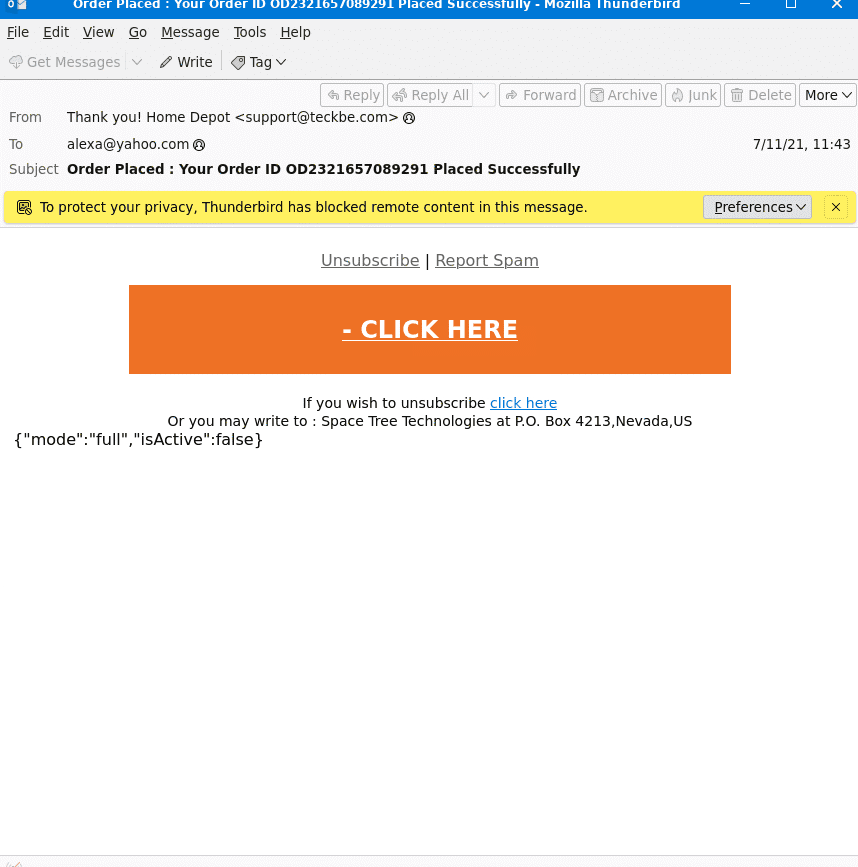
As you can see, the email is created so that it looks like it came from Home Depot.
Answer: Home Depot
The sender’s email is support@teckbe.com.
Answer: support@teckbe.com
Another easy one. Just read it from the subject line.
Answer: Order Placed : Your Order ID OD2321657089291 Placed Successfully
Copy the url from the email, and go to CyberChef. You can find a defang URL recipe on the left menu:
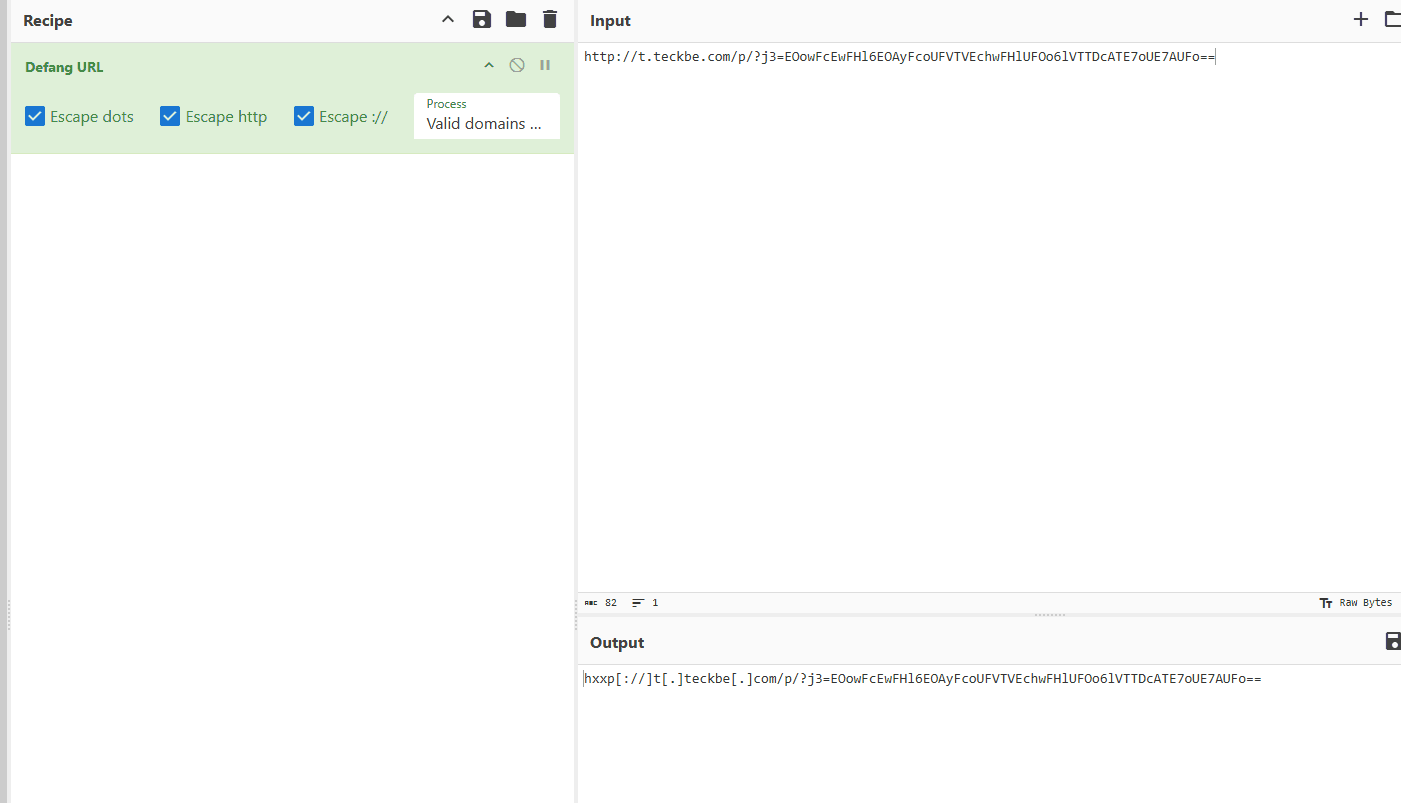
This makes it safe to share. You will do this defanging a lot in your future career!
Answer: hxxp[://]t[.]teckbe[.]com/p/?j3=EOowFcEwFHl6EOAyFcoUFVTVEchwFHlUFOo6lVTTDcATE7oUE7AUFo==
Before ending this room, you should know what BEC (Business Email Compromise) means.
A BEC is when an adversary gains control of an internal employee’s account and then uses the compromised email account to convince other internal employees to perform unauthorized or fraudulent actions.
Tip: You should be familiar with this term. I have heard this question asked before in a job interview.
Within this room, we covered the following:
In the upcoming Phishing Analysis series, we’ll look at samples of various common techniques used in phishing email campaigns, along with tools to assist us with analyzing an email header and email body.
Next room in this module: Phishing Emails 2
The answer is Business Email Compromise.
Answer: Business Email Compromise

Congratulations on completing Phishing Analysis Fundamentals. I hope you enjoyed this room. It was pretty basic, but nonetheless so important because phishing affects every on a daily business.
Come back soon for more walkthroughs of rooms on TryHackMe and HackTheBox, and other Cybersecurity discussions.
Find my other TryHackMe SOC Level 1 Path walkthroughs here.
Find my other walkthroughs here.
You are welcome to comment on this post, or share my post with friends.I would be even more grateful if you support me by buying me a cup of coffee:

I learned a lot through HackTheBox’s Academy. If you want to sign up, you can get extra cubes, and support me in the process, if you use the following link:
[…] Phishing Analysis Fundamentals […]